28 Review Model, Policies and Practices of Interpreter Referral Companies
Issue: Consumers and interpreters are not always clear about how interpreter referral companies operate
Proposed Solution: Interpreter referral companies in Minnesota are typically for-profit businesses. Each also has their ties with the communities served and holds deep values in their services. Multiple concerns are raised by DDBHH consumers and interpreters that relate to interpreter referral company practices and policies. With confidentiality, information sharing from referral companies is often restrained, increasing consumers’ and interpreters’ desires for transparency. Examples include: Requesting specific interpreters but being assigned a staff interpreter who is not preferred Inability for DDBHH consumers to know what is happening with their interpreting request, disconnect of consumer not having access to information about their own services Desire for DDBHH consumers to have access to more information about the interpreters on the company’s list – specializations, background knowledge and skills in the specific setting where they are assigned, seeing a sample of interpreter’s signing skills, etc. A working group from interpreter and consumer represented entities could develop a wish list of interpreter referral company practices and policies that would benefit them. Once this list is shared with companies, a response from each company would be shared with the communities impacted.
Expected outcome: More clarity of what interpreters and DDBHH consumers are seeking from interpreter referral companies. Transparent community conversations with interpreter referral companies who earn income from serving the DDBHH and interpreting communities.
Who is impacted: Consumers, interpreters
Timeline: 6 months
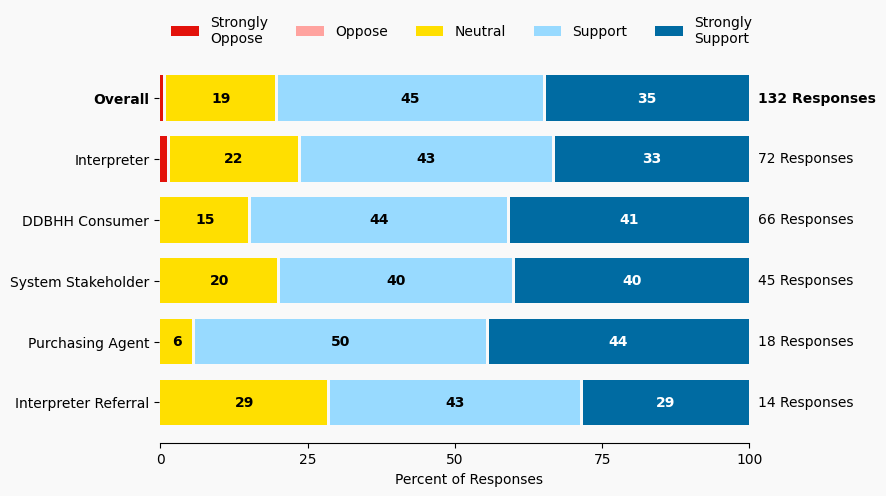
Summary of Support Image Description
The stacked bar charts show how respondents rated their level of support and the total number of responses. The percentage for the five support levels is shown from left to right: Strongly Oppose (Dark Red), Oppose (Light Red), Neutral (Yellow), Support (Light Blue), and Strongly Support (Dark Blue).
Respondents may identify with multiple subgroups. The overall level of support is:
Overall
Strongly Oppose: 1%
Oppose: 0%
Neutral: 19%
Support: 45%
Strongly Support: 35%
Click to see the detailed image description for each subgroup.
Interpreter
Strongly Oppose: 1%
Oppose: 0%
Neutral: 22%
Support: 43%
Strongly Support: 33%
Interpreter Referral
Strongly Oppose: 0%
Oppose: 0%
Neutral: 28%
Support: 43%
Strongly Support: 28%
DDBHH Consumer
Strongly Oppose: 0%
Oppose: 0%
Neutral: 15%
Support: 44%
Strongly Support: 41%
Purchasing Agent
Strongly Oppose: 0%
Oppose: 0%
Neutral: 6%
Support: 50%
Strongly Support: 44%
System Stakeholder
Strongly Oppose: 0%
Oppose: 0%
Neutral: 20%
Support: 40%
Strongly Support: 40%
Overview of Respondents Opting for In-Depth Solution Analysis
After indicating their support level, 6% of the 132 respondents opted in to further assess whether the solution would worsen or improve on five metrics. Of the opt-in reviewers (8 respondents), 87% supported the solution, 12% were neutral on the solution, and 0% opposed the solution.
The remaining 124 respondents did not opt in to further assess the solution. Of these people, 79% support the solution, 19% were neutral on the solution, and 0% opposed the solution.
Reviewer Evaluation of Solution Effectiveness

Solution Effectiveness Image Description
The stacked bar charts show how respondents assessed the effectiveness of this solution based on five metrics. For each metric, the percentage of respondents is shown from left to right: Worsens (Red), Improves (Blue), No Impact (Gray).
DDBHH Quality of Life
Makes It Worse 0%
Makes It Better 100%
No Impact 0%
Interpreter Satisfaction
Makes It Worse 0%
Makes It Better 85%
No Impact 14%
Consumer Choice
Makes It Worse 0%
Makes It Better 100%
No Impact 0%
Interpreting Availability
Makes It Worse 0%
Makes It Better 87%
No Impact 12%
Interpreting Quality
Makes It Worse 0%
Makes It Better 87%
No Impact 12%
Reviewer Feedback and Insights
Interpreter
Comments from Interpreters suggest a review of interpreter referral companies is necessary to ensure that they meet the needs of both interpreters and consumers. Concerns include ensuring that policies promote fair treatment of interpreters and do not prioritize profit over service quality. Suggestions include increasing transparency and accountability within the referral companies.
Deaf, DeafBlind, Hard of Hearing
Comments from DDBHH Consumers express the need for more transparency in the operations of interpreter referral companies. Concerns include ensuring that referral companies prioritize the needs of the Deaf community rather than profit. Suggestions include creating policies that promote inclusivity and accessibility.
System Stakeholder
Comments from System stakeholders suggest that referral companies should be reviewed to ensure that they are operating fairly and transparently. Suggestions include involving the Deaf community in the review process to ensure their needs are being met. Concerns include ensuring that the companies provide high-quality services to consumers.
PREVIOUS SOLUTION
27 Establish Grievance Process for Quality Control – Restorative and Timely Process
Issue: When something goes poorly in an interpreting setting, there are multiple considerations and perspectives. Sometimes there is gross negligence or incompetence on the part of the interpreter, and someone is grievously harmed. However, many concerns about interpreter performance could be resolved and harm repaired without legal or exhaustive and sometime ineffective processes. Constructive solutions rather than harsh or destructive penalties would not only be more humane but could also build the understanding and skill of working interpreters. A restorative approach would seek to make right whatever harm has been done and repair and strengthen relationships.
NEXT SOLUTION
29 Establish a Code of Professional Conduct for Interpreter Referral Companies
Issue: Multiple concerns have been raised about interpreter referral company practices. There is no standardization of interpreter referral companies statewide or nationwide. RID and NAD have each discussed and held groups to work on developing standards, such as a Code of Professional Conduct, Better Business Bureau ratings, or similar system for providing guidance to interpreter referral companies. No such systems or guidance currently exist.
Leave a Reply